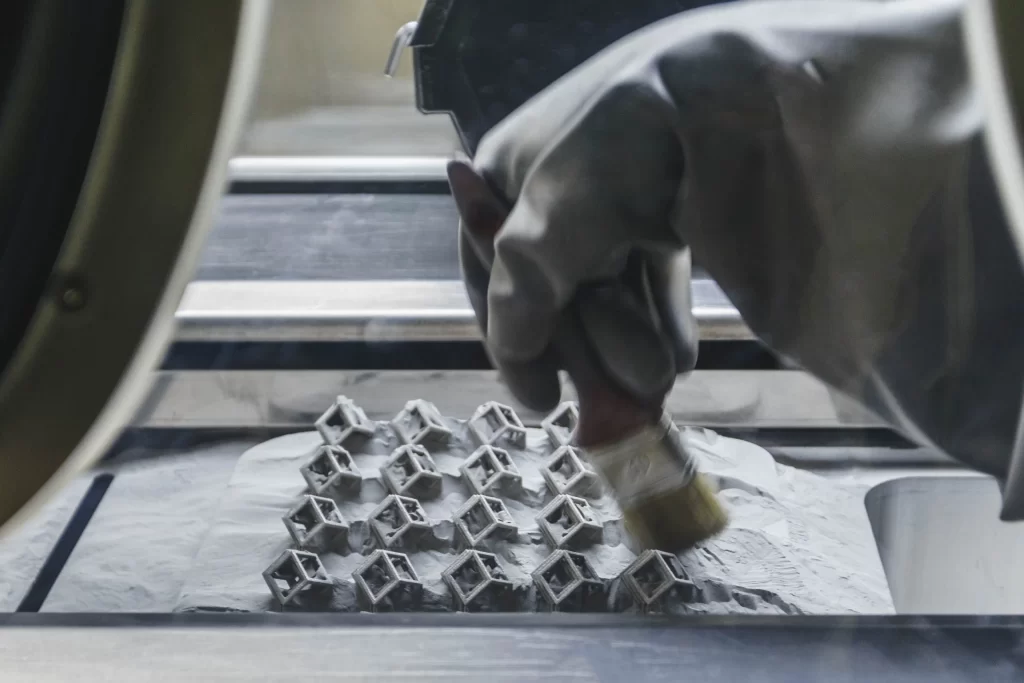
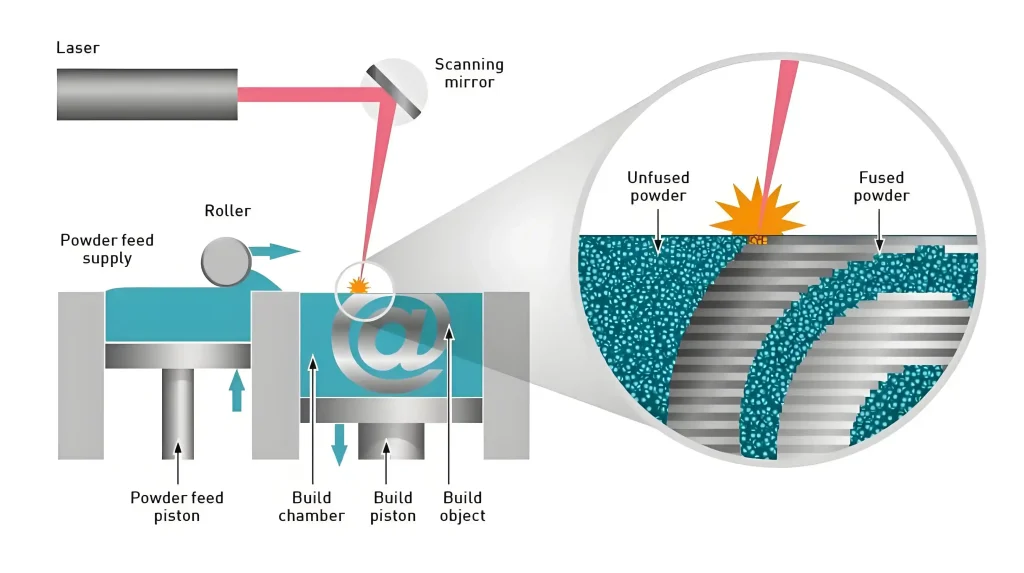
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is a modern technology that uses lasers to melt powdered materials into solid shapes. This technology allows for the creation of relatively fine, strong, lightweight and scrap-free parts. The process is used in industries such as aerospace, automotive and healthcare.
Currently, 27% of the companies in the market are using SLS 3D printing technology to manufacture their products, which shows the breadth and flexibility of this technology in the market.
Statistics show that the process is expected to grow from $3.2 billion in 2023 to $8.8 billion in 2028, demonstrating the importance of the process in product manufacturing.
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Definition and Overview
SLS 3D printing, also known as selective laser sintering, is an additive manufacturing process. It uses an intense laser to melt powdered materials into solid shapes. Such a method allows objects to be manufactured layer by layer, creating fine designs with little waste.
What makes this process unique is that it uses strong materials such as nylon. These materials allow for the production of strong, lightweight parts. For example, NASA and some private aerospace companies use this technology to manufacture parts. BMW also utilizes this technology to produce 150,000 parts per year, which demonstrates its utility for large industries.
Key Features of SLS 3D Printing
SLS 3D printing has unique features that set it apart from other methods:
- Powder sintering process:It utilizes a laser to heat and join powder particles. This allows complex shapes to be created without the need for additional support. The rest of the powder maintains its shape during the printing process.
- Material Efficiency:SLS wastes very little material. The powder left over after printing can be reused, which is also very environmentally friendly.
- High Precision:The fine powder material is sintered into shape by a laser and then laid down in each layer so that each layer is very precise. This is why industries such as aerospace and healthcare use this process.
- Versatility:SLS can also be used with a variety of materials such as plastics and composites. This is also great for things like prosthetics and automotive parts.
- Scalability:The process is laid up through each layer, making it very easy to work with, unlike other processes that require multiple operations. Whether you need one part or thousands, SLS can get the job done easily and quickly.
How SLS 3D Printing Works
The Role of Lasers
Lasers are very important in SLS 3D printing. Strong lasers (e.g. CO₂ lasers) move over the powder layer. The laser heats and connects the powder particles according to the 3D design. Only the desired part is melted, the rest is left untouched. The precision of the laser results in a solid and detailed end product.
Sintering of powdered materials
Sintering is the process of heating a powder so that it sticks together without melting. In SLS, the laser heats the powder below the melting point. This creates strong and durable parts. For example, nylon (PA12) is very strong, with a tensile strength between 35 and 55 MPa. However, tiny holes inside the part reduce the part’s ability to stretch, which is a disadvantage.
Layer-by-Layer Manufacturing
SLS can only manufacture one thin layer at a time. First, a layer of powder about 0.1 to 0.2 millimeters thick is applied. The laser then melts the shape of the layer. The platform is then lowered and a new layer of powder is added. This is repeated until the object is complete. The excess powder around the part acts as a support. This makes it possible to create complex shapes such as moving parts or hidden channels.
Components of an SLS 3D Printer
The SLS printer consists of several major components that work in tandem:
|
Component |
Function |
Importance |
|---|---|---|
|
Laser System |
For creating lasers to melt powders |
Used to make strong and detailed parts. |
|
Scanner System |
Lead Laser Accuracy |
Ensures precise shape without additional support. |
|
Build Chamber |
Areas where parts are manufactured |
Keep the conditions stable to obtain good quality. |
|
Recoating Mechanism |
Spreads new powder layers |
Ensures better part layer uniformity. |
|
Powder Delivery System |
Provides powder to the recoater |
Keep the process uninterrupted. |
|
Control Unit |
Controls the printer’s settings |
Keeps parts consistent by adjusting important settings. |
|
Inert Gas Atmosphere |
Keeps the air inside safe during printing |
Stops the material from reacting with air, keeping it strong. |
|
Heating Elements |
Warms the powder bed before printing |
Reduces stress on the part and makes it less likely to warp. |
All of these components work together to make SLS printing more efficient. For example, lasers and scanners ensure precise shapes, while recoaters apply layers evenly. These features also make SLS the best choice for manufacturing high-quality parts.
Advantages of SLS 3D Printing
High Precision and Accuracy
The process produces a very precise product that is perfect for detailing. It uses lasers to ensure that every layer is accurate. For example, the CASA model has a beam placement error (BPE) of only 50 microns in the Y-axis. This is much better than older methods. Newer models, such as the Optima model, are reducing this error to 5 microns. This level of accuracy meets the stringent regulations of industries such as aerospace and healthcare.
Material efficiency and sustainability
SLS 3D printing technology uses materials wisely. Unlike older methods that waste a lot of material, SLS reuses the leftover powder over and over again. This not only reduces waste, but also saves money. It also saves more resources by not requiring additional support structures.
A recent report shows that SLS is not only fast and environmentally friendly. It also makes good use of space and utilizes lasers to scan quickly. This speed not only saves a lot of time and energy, but it is also very good for the environment. Choosing SLS 3d printing services can help you be sustainable while manufacturing your products.
Complex geometries without support structures
The SLS 3D printing process creates complex shapes without the need for additional support structures. During the printing process, the remaining powder acts as a natural support.
Parts made with SLS are strong in all directions. The bonding between each layer is excellent so that the parts have the same strength everywhere. This also allows them to handle tough jobs.
Cost-effective prototyping and production
SLS 3D printing is a much less expensive manufacturing method. Older methods such as injection molding require expensive molds and tools. These high costs can be problematic for small production runs or new designs.SLS omits these steps. It allows parts to be made directly from digital drawings. That’s why it’s ideal for rapid prototyping and low-volume production.
SLS also saves money by reducing production costs. Studies have shown that it can reduce costs by up to 70%. This is because SLS wastes less material and works faster. The powder left over from a process can be reused, which saves on material costs.
Another big advantage is speed. It can produce prototypes or parts in hours or days. Whereas older methods can take weeks. This fast process saves time and money, especially when testing designs. It can help you complete projects faster and reduce overall costs.
Applications of SLS 3D Printing
Aerospace Industry
Lightweight, Durable Components
In the aerospace industry, where lightweighting of components is essential to improve fuel efficiency and performance, SLS 3D printing technology can produce robust, lightweight parts with detailed designs. It can create shapes that could not be made with older methods. For example, Airbus uses SLS to make high-temperature alloy parts. These parts are lightweight but tough enough for flight conditions. That’s what makes SLS the preferred choice for making parts for airplanes and spacecraft.
Key benefits:
Lighter parts save fuel and money.
Flexible design allows for creative solutions.
Rapid prototyping
SLS 3D printing technology also facilitates rapid prototyping for testing. This is very useful in the aerospace sector where time and accuracy are very important. Engineers can quickly test many designs to meet safety regulations. Rapid testing reduces costs and speeds up development. This is also something that helps aerospace companies stay ahead of the curve.
Medical Industry
Customized Implants and Prosthetics
The medical field uses SLS 3D printing to customize implants and prosthetics. These implants and prosthetics are made on a case-by-case basis for each patient. This improves comfort and results. For example, the implants can be perfectly matched to the desired size, thus reducing risks. The demand for these customized devices is growing and the market is expected to reach $6.6 billion by 2031.
Advantage:
Better fit improves the way the device works.
Faster recovery helps patients heal faster.
Medical Device Prototyping
SLS 3D printing can also be used to create models of medical devices. These models are not only useful for surgical planning or device testing, but can also be quickly modified to improve the design.SLS is ideal for healthcare because it can accommodate both small and large scale production needs.
|
Year |
Market Value (USD) |
CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 |
1.7 billion |
N/A |
| 2031 |
6.6 billion |
16.3 |
Automotive
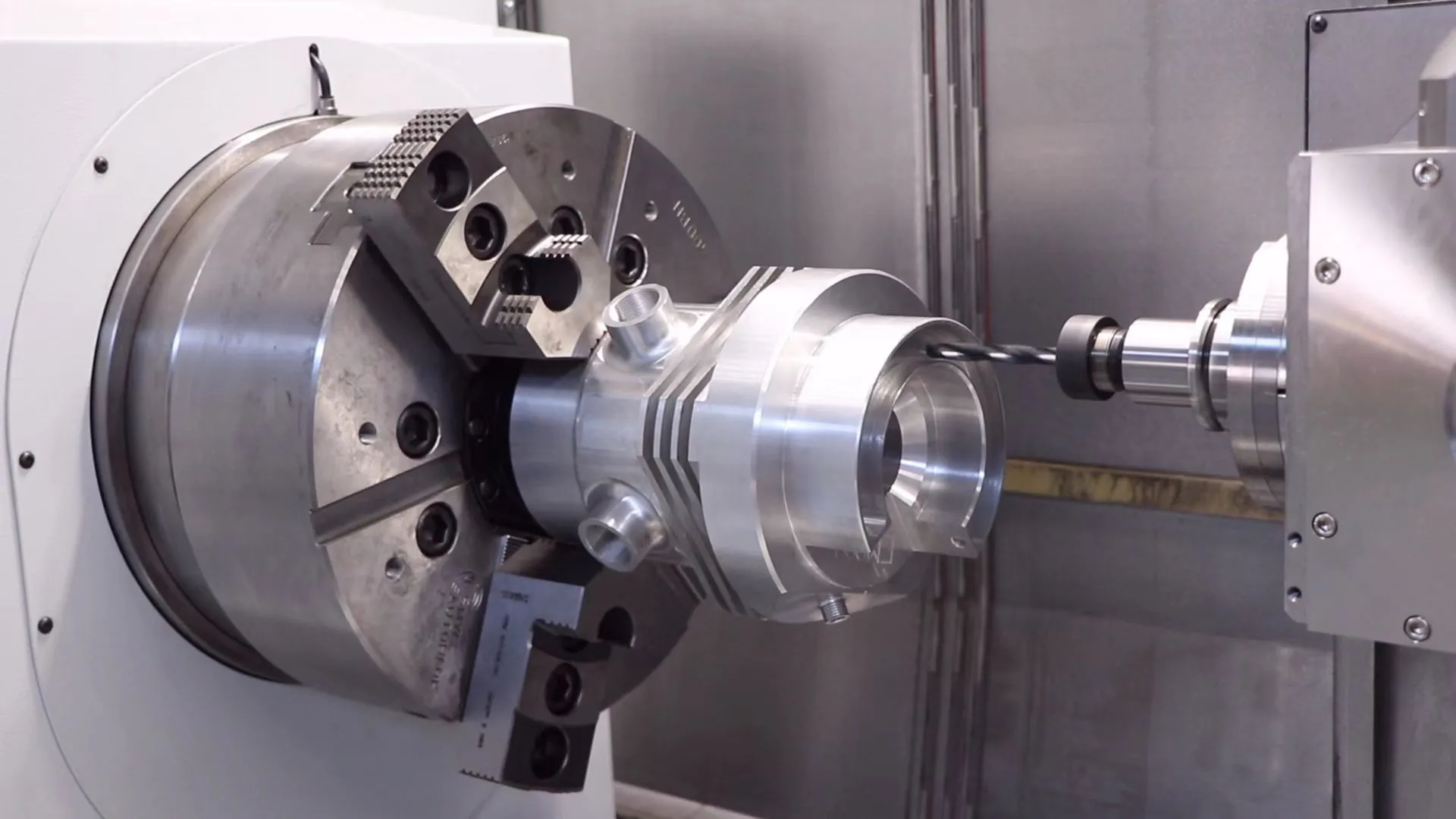
Functional prototypes
In the automotive sector, SLS printing can be used to create working prototypes. These prototypes are tested under real-world conditions to check performance. This helps companies to identify problems early, saving time and money. Porsche uses SLS to make rare replacement parts, which demonstrates the practicality involved.
Key benefits:
Faster production speeds up design work.
Easily customized to meet specific needs.
End-use parts
It can also be used to make automotive parts. These parts are precise and durable, making them ideal for automotive use. It’s perfect for small batches or customized orders. Automotive companies like SLS also because it produces high-quality parts quickly.
|
Industry |
Application Description |
Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Aerospace |
Aerospace companies use SLS to manufacture complex heat-resistant components. |
Lighter components save fuel. |
|
Automotive |
Porsche uses SLS to replace rare car parts. |
Faster production and easier customization. |
|
Healthcare |
SLS can produce customized implants and surgical planning models. |
Make patients more comfortable and heal faster. |
Consumer Products
Customized Products
SLS 3D printing technology has changed the way we make personal items. It allows you to design a phone case, jewelry or shoes to fit your style. You can easily change shapes, sizes and patterns using digital designs. Unlike older methods, SLS does not require molds or tools, making it perfect for creating one-of-a-kind items.
Nowadays, people want their products to express their individuality, and SLS 3D printing meets this need with flexibility and precision.New improvements in SLS make it easier to create sturdy, high-quality customized products.
Challenges of SLS 3D Printing
High Initial Costs
The upfront costs of getting started with SLS 3D printing technology are high. Purchasing equipment, installation and training staff can be a significant expense. Commercial printers require a large investment, while DIY kits are less expensive but difficult to use.
Costs include:
Installation: Some printers require an expert to install.
Training: Workers need to be trained to use the machine well.
Space: Printers require adequate space and good air circulation.
Safety Equipment: Materials such as nylon may require protective equipment.
These costs make it difficult for small businesses or individuals to afford SLS. So choosing the right manufacturer is a good decision.
If you need high-quality SLS 3D printing services, Future Parts is the place to go. They offer a wide range of services which include solutions, the most important of which is fast turnaround.
Limited Material Choices
SLS 3D printing does not offer a wide range of materials like older methods. This limits the part’s workability and range of use. Example:
Some materials, such as titanium, require special conditions to avoid problems. Without these conditions, parts may develop air bubbles or rough surfaces, making them less strong.
Not all metals and plastics can withstand the temperatures of SLS. This makes it difficult to match material properties to part requirements. Sometimes you have to choose between strength and availability.
Post-processing requirements
The work doesn’t stop when 3d printing is over. Post-processing is required to make the part ready for use. Examples include
Powder cleaning: Powder can stick to the inside of the part and needs to be removed.
Complex Shapes: Tiny features, such as channels, need to be cleaned manually.
Industrial CT Scans: These scans check for hidden defects and ensure accuracy.
Without these steps, parts can be damaged or fail during use. Post-processing takes time and effort, especially for detailing. So planning is necessary.
Conclusion
In summary, SLS 3D printing is a precise, efficient, and versatile technology that not only makes complex, durable parts. It also minimizes material waste and produces high-quality parts. Whether you need complex or mass-produced parts, it can meet your needs.