Aluminum extrusion is done by extruding aluminum into a die, resulting in a profile with a cross-sectional design. It supports industries such as construction and electronics.
- In 2023, more than 60% of aluminum extrusion funding comes from construction projects, driven by housing growth.
- The automotive sector has a market value of $10,818 million in 2021. This is expected to double by 2030.
- Global demand is likely to grow the market size from $69 billion in 2020 to $95 billion by 2030.
Its flexibility and growth are also key to making aluminum extrusion a modern manufacturing industry.
What Is Aluminum Extrusion?
Definition and Overview
Aluminum extrusion is a method of forming aluminum. It squeezes aluminum through a die called a “mold” to make long, identically shaped bars. This method can produce simple bars as well as elaborate designs. These aluminum profiles are also widely used in many industries such as construction, automotive and electronics.
Over time, the process has been improved with advances in technology and the need for lighter materials. Here are some of the important changes in the aluminum extrusion process:
- Automakers wanted lighter parts, which led to new extrusion concepts.
- Engineers now use methods such as bending and hydroforming to create complex shapes.
- Studying the behavior of aluminum during extrusion helps make better products.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Laboratory Tests | Check how processing changes aluminum’s properties. |
| Microstructural Analysis | Studies how heat affects aluminum during extrusion. |
| Crystallographic Study | Looks at grain patterns using special tools. |
| Stress Analysis | Measures stress and heat for accurate shaping. |
These improvements are also what make aluminum extrusion a powerful and practical option for modern factories.
Why Aluminum Is Ideal for Extrusion
Aluminum is well suited for extrusion because of its special properties. It is lightweight and strong, making it ideal for products such as automobiles and aircraft. For example, untreated 6061 aluminum has a strength of 241 MPa, while heat-treated 6061 aluminum has a strength of 310 MPa. This also means that it is strong without being bulky.
Aluminum is also easy to shape into complex designs without breaking. Adding magnesium or silicon can make it even stronger. Some advanced materials, such as aluminum matrix composites (AMCs), mix aluminum with ceramic particles for added strength.
Another advantage of aluminum is its resistance to rust and corrosion. The natural protective coating on the surface of aluminum prevents corrosion, making it ideal for use outdoors or near water. In addition, aluminum can be recycled, which is good for the environment.
How Aluminum Extrusion Works
Preparing the Aluminum Billet
The first step is to prepare the aluminum billet. Billet is a solid block of aluminum used as a raw material. You can choose the right alloy for your product. alloys such as 6061 or 6063 are popular. Alloys such as 6061 or 6063 are popular because they are strong, rust-resistant and easy to shape.
Next, the billet is cleaned to remove any dirt or impurities. This enhances the production of a smooth, flawless product. After cleaning, the billet is cut to the proper size. The size must match the extruder. This step is critical for efficiency and quality.
Heating Aluminum
When ready, heat the aluminum billet to allow it to soften. The temperature is set between 750°F and 900°F. This will make the aluminum easier to form without melting.
The heating must be precise. Too low a temperature and extrusion will be more difficult. Too high a temperature and the metal will become brittle. Larger billets save energy during the heating process. For example, a 1.6 kg billet uses 30% less power than a 1.3 kg billet. The surface of the alloy and the walls of the crucible affect heat transfer. The alloy has an emissivity of 0.03, while the crucible wall has an emissivity of 0.99 due to the roughness of the oxide layer.
| Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
| Melting efficiency | 1.6 kg billet uses 30% less power than 1.3 kg billet. |
| Skull weight | Skulls weigh 178 g, about 13% of the alloy’s starting mass. |
| Alloy emissivity | Alloy emissivity is 0.03, higher than expected values. |
| Crucible wall emissivity | Crucible walls have 0.99 emissivity due to oxide layers. |
| Power input effect | More power reduces skull weight, showing power affects efficiency. |
Careful heating ensures that the aluminum can be formed.
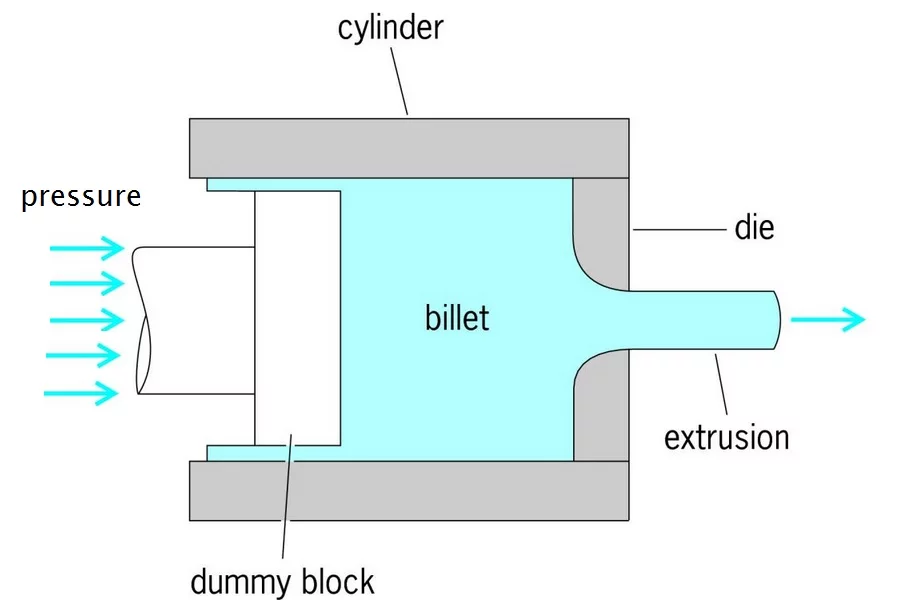
Pushing Aluminum into the Die
After heating, the aluminum billet is fed into the extruder. Hydraulic cylinders push the aluminum billet into the steel die. The steel die extrudes the aluminum billet into the desired shape.
The aluminum flows out of the die at a speed of 50 meters per second. This high speed makes the process fast, but requires precise temperature control. Liquid nitrogen cooling is used to control the temperature. This type of cooling extends the life of the mold and improves product quality.
- Liquid nitrogen cooling is now widely used.
- Cooling channels in the mold can increase efficiency and speed.
- Proper cooling prevents defects such as cracks or warpage.
By controlling pressure, speed and temperature, you can achieve high quality aluminum shapes. Future Parts offers complex and volume aluminum extrusion services.
Profile Cooling and Machining
After aluminum leaves the mold, it must be cooled before it can be processed. Cooling is important to maintain shape and strength. Depending on the alloy and product requirements, cooling can be done with air or water.
Once the aluminum has cooled, it needs to be stretched to repair bends and twists.
Next, the aluminum is cut into smaller pieces. Cutting tools allow for neater edges.
The final step is finishing. This improves the appearance and performance of the aluminum. Surface finishing processes include
- Anodizing: Adds a protective layer to prevent rust.
- Powder Coating: Covers the surface with a strong, colorful coating.
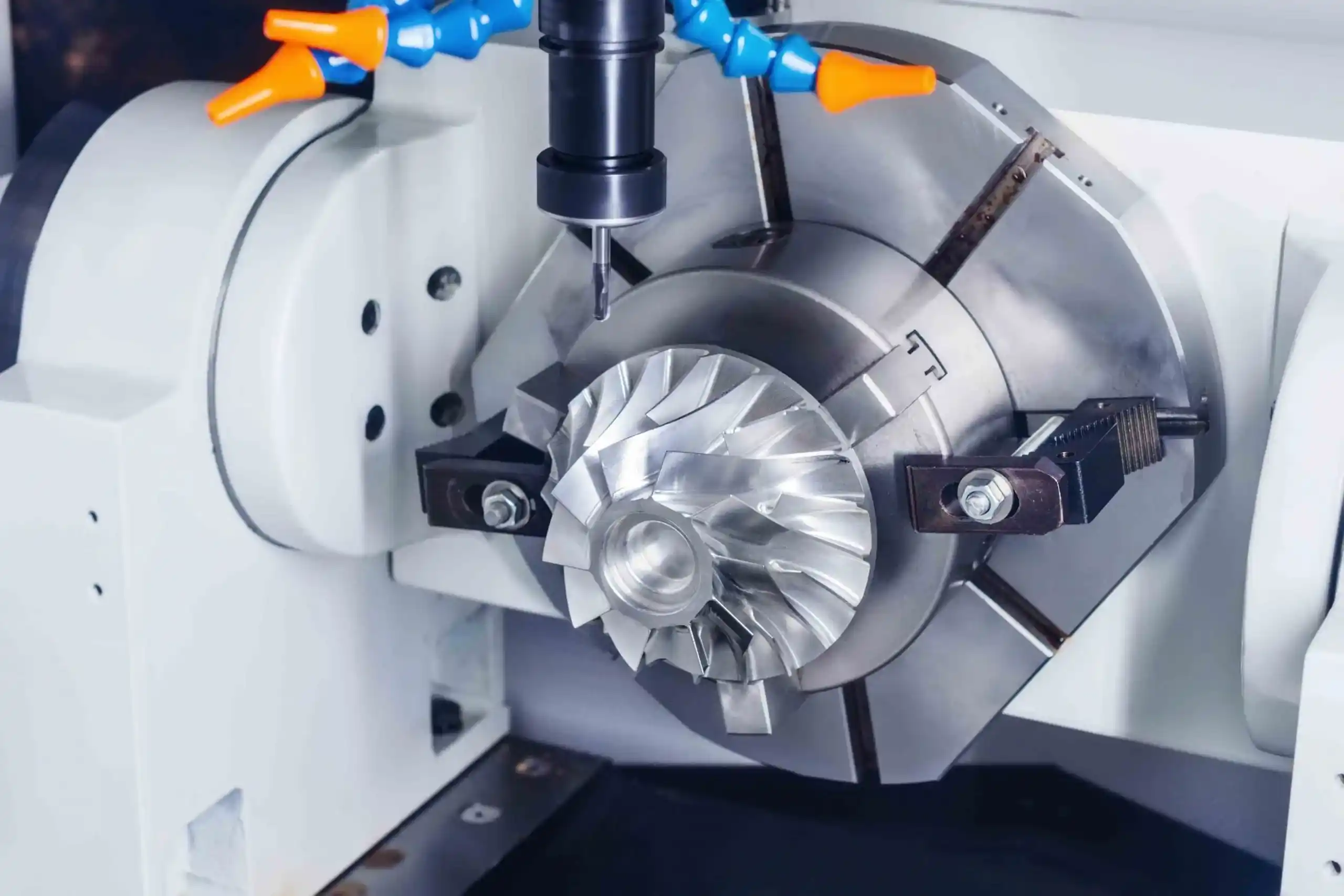
- Machining: Drilling or milling aluminum profiles to fit a specific design.
Once machined, the aluminum is ready for use.
Benefits of Aluminum Extrusion
Lightweight and Strong
Aluminum extrusions are both lightweight and strong. Aluminum is much lighter than steel, which helps reduce weight. This is critical for fuel savings and performance in cars and airplanes. Aluminum may be light, but it’s tough as steel. Heat-treated alloys like 6061 can withstand forces up to 310 MPa, making them extremely durable.
Adding magnesium or silicon can also make aluminum even stronger. Advanced materials such as aluminum matrix composites increase toughness. The combination of light weight and high strength is what makes aluminum extrusion so popular in modern factories.
Corrosion Resistant
Aluminum extrusion works well in areas prone to rust. Aluminum forms a natural protective film that protects it from damage. This protective film prevents rusting and maintains the strength of aluminum in harsh conditions.
Compared to steel, aluminum offers better resistance to rust and corrosion, especially in wet or salty areas. In tropical or marine environments, treatments such as anodizing can further enhance protection. These treatments can make aluminum more durable.
- The natural layer of aluminum prevents rust.
- Treatments such as anodizing provide additional protection in harsh locations.
- Aluminum lasts longer than steel in wet or salty areas.
Cost-Effectiveness
Aluminum extrusion is an economical way to make strong, lightweight products. The process forms aluminum with virtually no scrap, which saves on material costs. It is an ideal choice for projects (large or small) with tight budgets.
Different extrusions are available to meet different needs:
- 2020 Aluminum extrusions: for lightweight and low-cost projects.
- 4040 Aluminum Extrusions: best suited for medium-sized projects that require stability.
- 8020 Aluminum Extrusions: Designed for heavy machines and large loads.
Studies have shown that the aluminum extrusion process is more cost-effective than other processes. Its increasing use has proven its affordability and practicality. As the industry grows, aluminum extrusion continues to be the smart choice for manufacturers around the world.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Technique | Shapes aluminum into exact forms with little waste. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Great for strong products at lower costs. |
| Market Demand | Increasing due to more people and industry needs. |
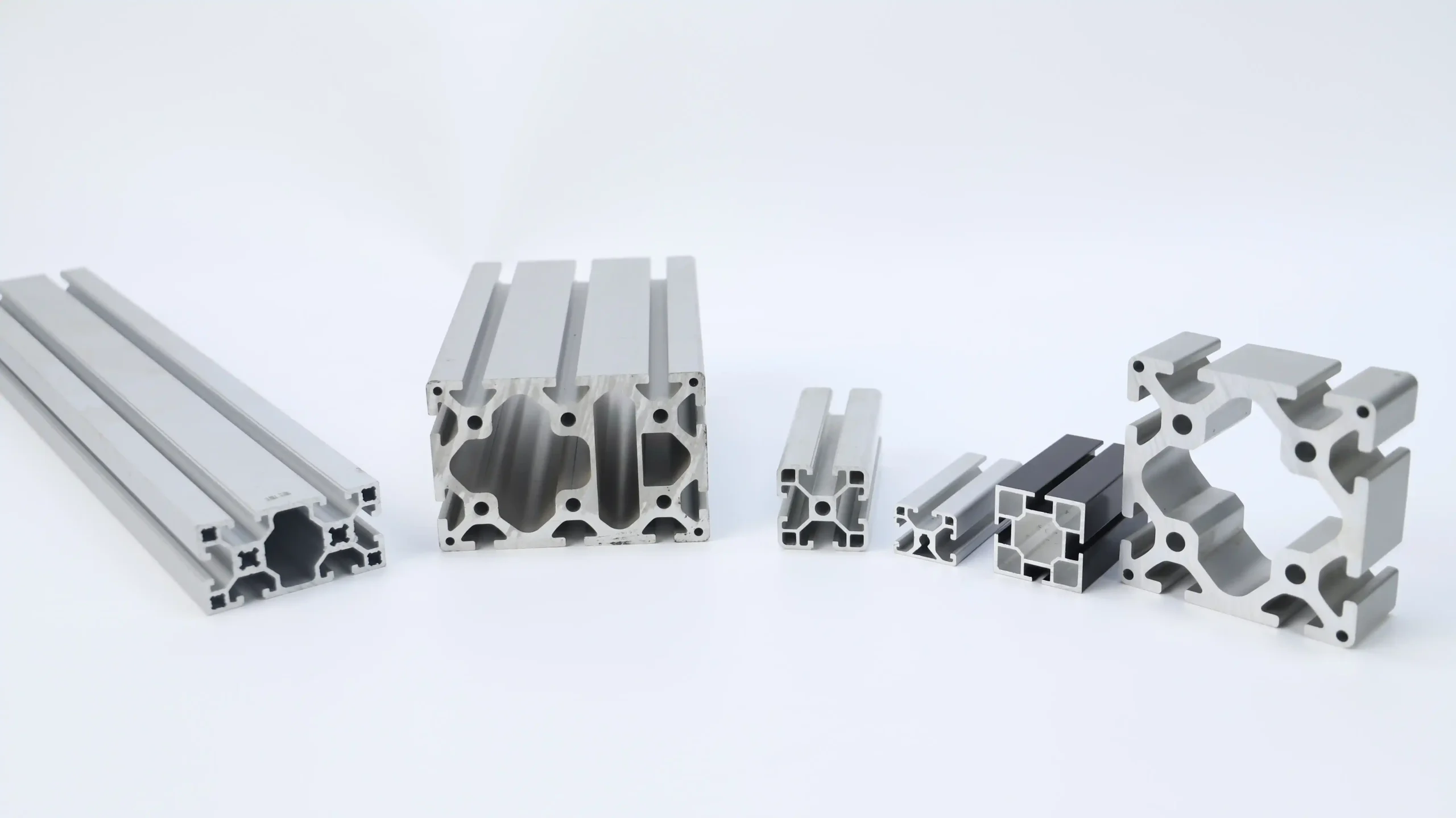
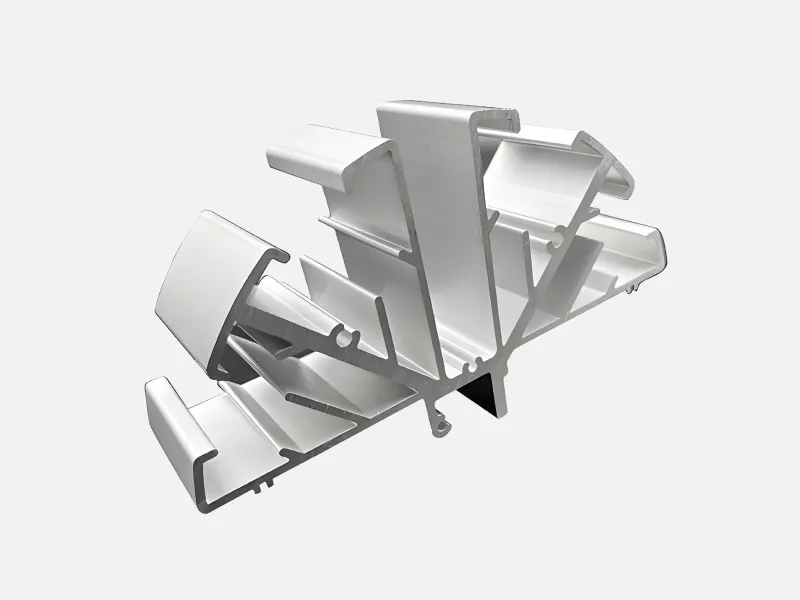
Types of Shapes in Aluminum Extrusion
Aluminum extrusion can be formed into many different shapes that can be used for different purposes. It offers standard and customized designs that combine flexibility and accuracy.
Standard Shapes
Standard shapes are common profiles used in many industries. These simple shapes include:
-
Angles: L-shaped pieces used for structural support.
-
Channels: U-shaped pieces used for frames or rails.
-
Tubes: Strong and lightweight hollow cylinders.
- Bars: solid square or rectangular pieces used for general tasks.
These shapes are popular in construction, transportation and consumer goods. They are ideal for mass production and are very affordable. If you need a quick and affordable option, standard shapes are a good choice.
Customized Configuration Files
Custom profiles allow you to design shapes for specific applications. They are perfect for industries such as aerospace, electronics or construction. An engineer can help you create a profile that meets your exact needs.
For example, custom profiles may have fine curves or cut-out sections to reduce weight. These designs can improve the appearance and functionality of your product. While custom profiles cost more than standard profiles, they offer great flexibility.
Surface Treatment
Surface treatments can make aluminum look better and last longer. You can choose from several options depending on your needs:
- Brushed: Normal surface, simple to use.
- Anodizing: Adds protection against rust and improves appearance.
- Powder Coating: Gives a strong, colorful finish.
- Polished: gives a shiny, smooth surface with a premium look.
These finishes protect aluminum and make it more attractive. For outdoor or visible projects, the finish is very important.
Applications of Aluminum Extrusion
Construction and Architecture
Aluminum extrusions are common in the construction industry because it is strong and durable. It is lightweight, 65% lighter than steel, but still strong and durable. Builders use it to make window frames, door frames, and solar panel brackets. These components are rust-resistant and long-lasting, even in harsh weather.
Aluminum reflects heat and light, which can help conserve building energy and thus reduce cooling costs. New window systems further enhance energy savings. Aluminum profiles are now a key material in modern building design.
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Lightweight and Strong | Lowers weight but stays durable. |
| Corrosion-Resistant | Lasts longer outdoors or near the sea. |
| Reflective | Saves energy by reflecting heat and light. |
| Flexible | Fits many designs without losing strength. |
Automotive and Transportation
In the automotive sector, aluminum profiles reduce the weight of cars. Lighter cars use less fuel and emit fewer emissions, thus contributing to environmental protection. Automakers use aluminum in frames, panels, bumpers and engine components.
Demand for aluminum in transportation is growing rapidly. By 2034, the automotive aluminum extrusion market will reach US$167.67 billion. This shows how important aluminum is for environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient designs.
Electronics and Consumer Products
Aluminum extrusion is very useful in electronics. It dissipates heat well, making it ideal for cooling components such as radiators. It is also used to make housings that protect electronic components, which are both lightweight and strong.
In everyday products, aluminum extrusion is both practical and stylish. It is often used in furniture, sports equipment and home furnishings.
Conclusion
Aluminum extrusion is a flexible, efficient and cost-effective manufacturing method that is vital in today’s manufacturing industry. It creates parts that are lightweight, strong and environmentally friendly.Future Parts offers specialized aluminum extrusion services to help you bring your custom designs to life.
FAQ
What is the difference between standard and custom aluminum profiles?
Standard profiles are common shapes such as tubes and channels. Custom profiles are manufactured to meet specific needs and have a unique design. They cost more but work better in specialized applications as well.
What is the difference between aluminum and extruded aluminum?
Aluminum is the original metal, and extruded aluminum is aluminum that is shaped through a die to form specific profiles for use in construction, automotive, and other industries.
How do I choose the best extruded aluminum alloy?
Choose according to the needs of your project. alloys such as 6061 and 6063 are strong and rust-resistant. You can consult our experts to find the right alloy for your job.