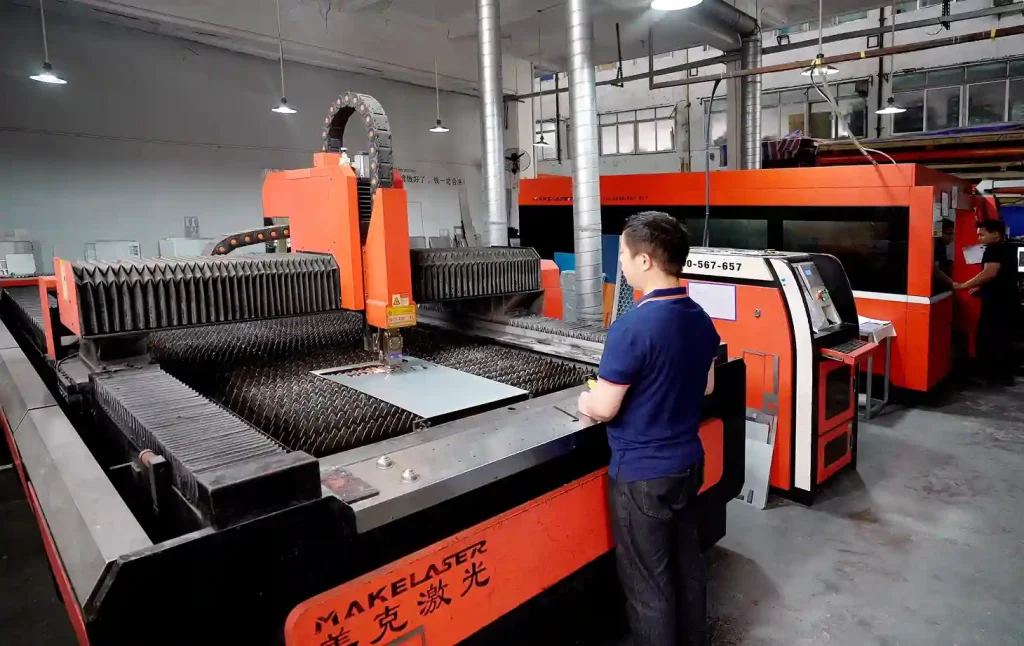
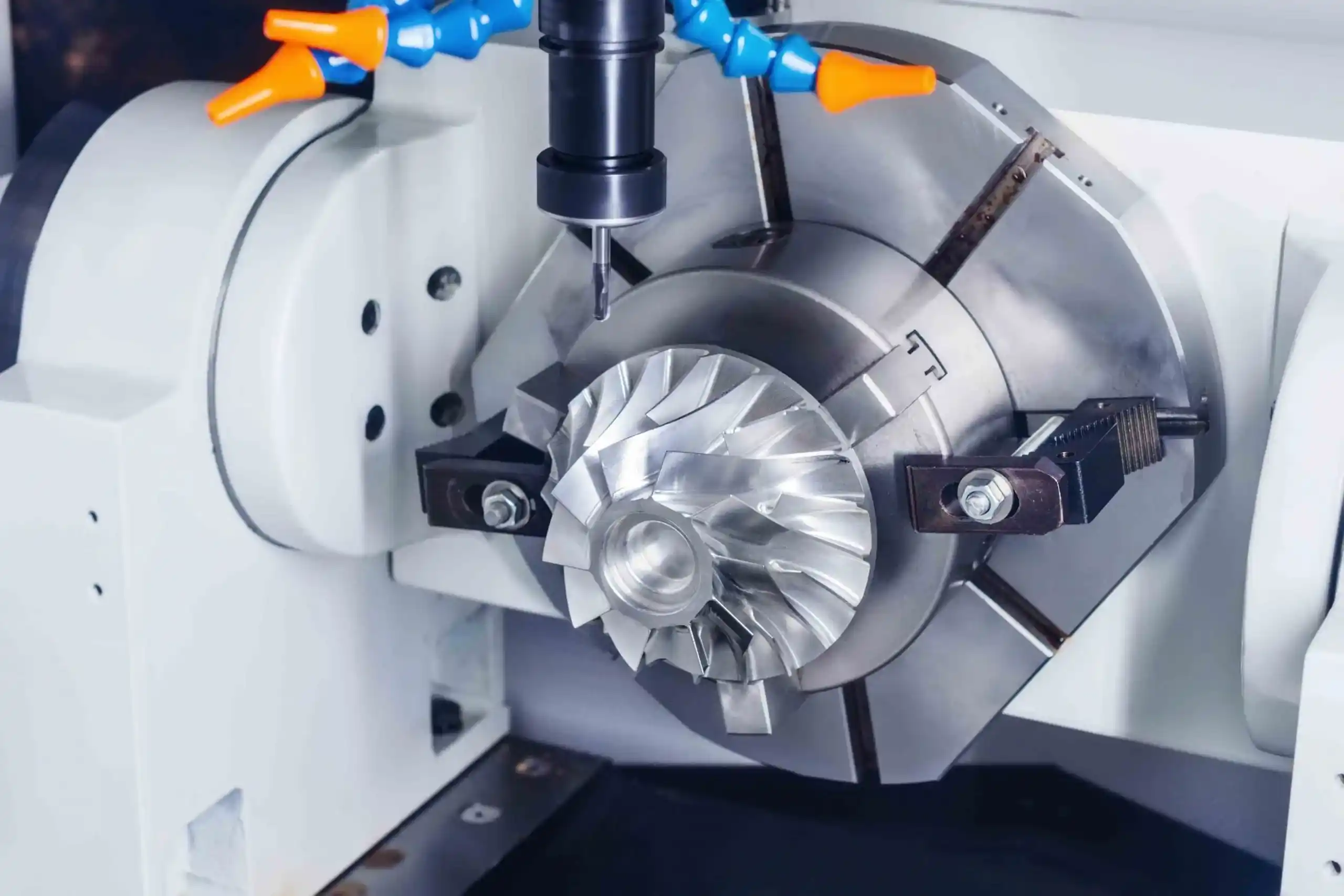
Sheet metal fabrication is the processing of flat sheet metal into useful parts. It uses meticulous shaping and molding methods. This process is very important in making items and buildings.
The industry is growing rapidly. The global market is likely to grow from $10.3 billion in 2024 to $15.2 billion by 2034. From 2022 to 2023, the production of automobiles alone will grow by 10.3%. Sheet metal fabrication is very flexible and can provide powerful customized solutions for many industries.
Key Takeaways
- Sheet metal fabrication processes flat sheet metal into useful components. This is done by cutting, bending and joining metals. It is very important in industries such as automobiles and airplanes.
- Choosing the right metal is very important. Steel is strong, while aluminum is lightweight. This extends the life of the product.
- Special methods such as laser cutting and CNC machining allow for faster and more precise work. These methods help create detailed customized designs.
- Surface treatment steps such as powder coating and anodizing make metal parts look better. They also prevent rust and damage to the metal.
- Understanding the processes and materials can help you make informed choices. This will result in a better product and save money.
What Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Definition and Overview
The process involves machining sheet metal into parts. It involves the use of cutting, bending and joining metals to produce a variety of parts. Making these parts also requires special tools and precision. Bending makes curves or angles, while cutting precisely shapes the metal.
This process is very flexible and important in modern manufacturing. It can be used to manufacture both small items such as electronic housings and large structures.The global sheet metal market was valued at $12 billion in 2022. By 2030, it could grow to $18 billion. This indicates the need for customized metal parts in industries such as automotive, aircraft, and construction.
Key terms in sheet metal fabrication include
- Material Selection: Selection of metal based on strength or rust resistance.
- Manufacturing Tolerance: Maintaining dimensional accuracy during the production process.
- Sheet Metal: Thin, flat pieces of metal used in a project.
Importance in Manufacturing and Construction
Sheet metal fabrication is key to the manufacturing and construction industries. It produces strong, lightweight components. It is relied upon in industries such as automotive, aircraft, and electronics. For example, custom fabrication shops account for 31.4% of revenue in 2023. Mechanical uses are growing rapidly, at a CAGR of 7.5%.
In construction, sheet metal is commonly used for roofing, piping, and framing. It is not only strong and flexible, but also aesthetically pleasing and functional. its importance in the construction sector is evident from the fact that the U.S. leads the market with a 75.2% revenue share in 2023.
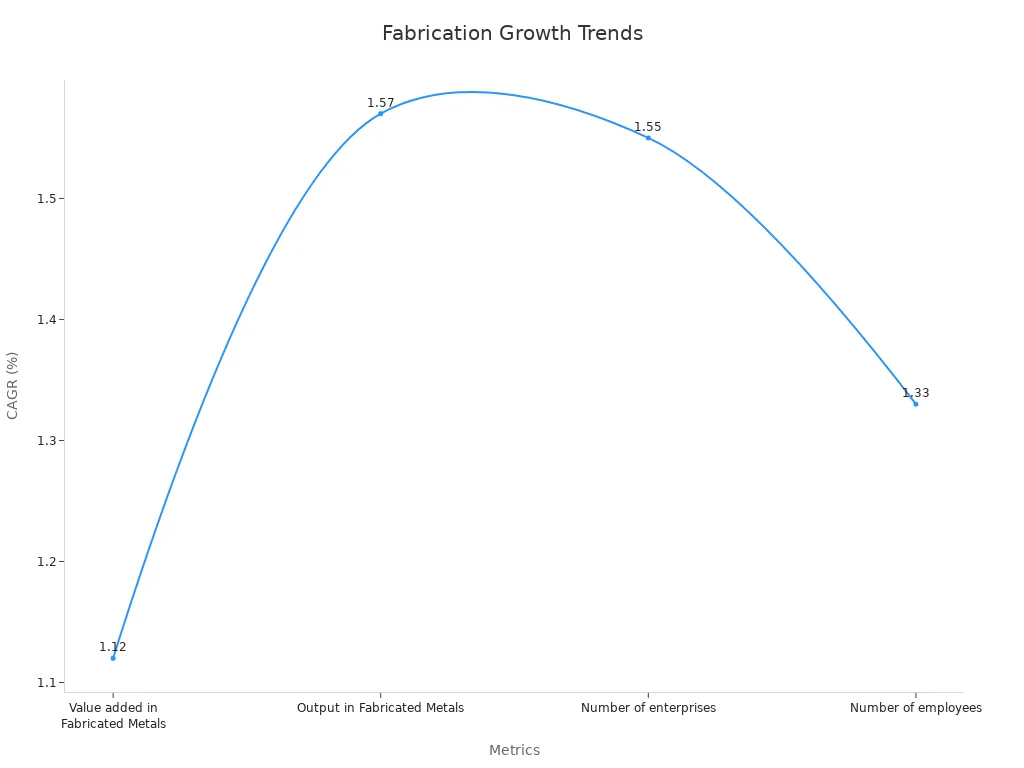
The table below shows key facts about fabricated metals:
| Metric | Value (2025) | CAGR (2025–2029) |
|---|---|---|
| Value added in Fabricated Metals | US$893.33bn | 1.12% |
| Output in Fabricated Metals | US$2.55tn | 1.57% |
| Number of enterprises | 904k | 1.55% |
| Number of employees | 11m | 1.33% |
This data shows how sheet metal fabrication helps industries grow and innovate.
The Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Design and Planning
Design and planning is the first step in manufacturing. Blueprints are produced to show dimensions, tolerances and materials. This ensures that the product is fit for its purpose. Engineers use methods such as DFMA or axiomatic design to improve the process.
DFMA simplifies the manufacturing and assembly process. Axiomatic design uses diagrams to relate design requirements to product features. Multi-objective optimization helps balance cost, material, and time. These methods use data to make processes better and more accurate.
| Methodology | What It Does | How It Uses Data |
|---|---|---|
| DFMA | Simplifies making and assembling products | Uses numbers in late design stages |
| Axiomatic Design | Matches design needs with product features | Uses charts to connect ideas |
| Multi-objective Optimization | Balances costs, materials, and time | Uses modules and charts |
| DFA Index | Checks how easy a product is to assemble | Uses tables and scores |
| Total Grade Indices | Rates how efficient the process is | Scores based on key factors |
Using these tools helps make the design process smooth and efficient.
Cutting and Shaping
Cutting and shaping processes flat sheet metal into parts. Methods used include stamping, laser cutting or waterjet cutting. Each method is suitable for different materials and designs.
For example: Stamping
- Stamping can be very precise, with tolerances ranging from ±0.001 inches to ±0.005 inches.
- Laser cutting has a tolerance of ±0.004 inches to ±0.008 inches.
- Waterjet cutting tolerances range from ±0.001 inches to ±0.008 inches.
Accuracy is very important in this process. Tolerances are typically between ±0.005 inches and ±0.015 inches. This ensures that parts fit together perfectly.
| Cutting Method | Tolerance Range |
|---|---|
| General Cutting | ±0.062 inches |
| Precision Sheet Metal | ±0.005 to ±0.015 inches |
| Stamping | ±0.001 to ±0.005 inches |
| Laser Cutting | ±0.004 to ±0.008 inches |
| Waterjet Cutting | ±0.001 to ±0.008 inches |
Choosing the right cutting method ensures the needed precision for your project.
Forming and Bending
Forming and bending shapes metal into curves or angles. Special tools are used to bend the metal without breaking it. The bend radius is very important in this step. It allows the metal to be bent as far as it will go without damage.
Keeping the bend radius consistent can prevent problems such as cracks or springback. If the radius is too small, the metal may crack. If the radius is too large, kickback can make it difficult to get the correct angle.
Planning is the key to balancing strength and ease of bending. By controlling the bending radius, you can create parts that look good and work well.
Joining and Assembly
Joining and assembly are critical steps in manufacturing metal products. These steps join parts together to form a complete product. The method of joining depends on the material, the application and the strength required.
Here are some common joining methods:
| Joining Method | Benefits | Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Riveting | Rugged, durable and can handle vibration well | Cars, planes, factories |
| Welding | Strong bond, resistant to loads and vibrations | Heavy-duty industries |
| Clinching | Handles mechanical stresses without heating | Industrial purposes |
| Pressure Rivet Assembly | Robust, permanent and suitable for mass production | Large-scale manufacturing |
Each method has its own advantages. For example, riveting is suitable for use in cars and airplanes because it can withstand vibration.
Welding has high bond strength and is ideal for heavy duty work. Riveting also avoids heat, making it suitable for heat-sensitive materials. Pressure rivet assembly is suitable for making many items quickly.
When choosing a joining method, you need to consider the needs of the project. Consider factors such as strength, the environment and the quantity to be made.
Finishing and Surface Treatments
Surface treatments can make metal look better and last longer. These steps also protect the metal from rust and improve its appearance.
Common surface treatments are:
- Powder Coating: Adds color and protects against scratches and rust.
- Anodizing: Protects against rust and adds a decorative layer, suitable for aluminum.
- Electroplating: Adds a thin metallic layer for a more attractive and durable appearance.
- Polishing: Removes imperfections and makes the surface smooth and shiny.
Surface quality is checked using these measures:
| Measure | What It Means |
|---|---|
| Ra | Average roughness of the surface, measured in micrometers or microinches. |
| RMS | Square root of average deviations from the surface line, also in micrometers. |
| Rt | Total height between the highest and lowest points on the surface. |
Lower Ra values mean smoother surfaces, which are important for things like medical tools or electronics.
Techniques Used in Sheet Metal Fabrication
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a fast, precise method of cutting metal. It utilizes a powerful laser beam to cut it. This method is perfect for creating fine shapes and small holes. The edges are smooth, so less finishing is required.
This process also reduces waste. It saves money by using more than 94% sheet metal. Laser cutting is very fast, up to 1200 inches per minute. This makes it perfect for quickly manufacturing many parts.
Here’s how laser cutting compares to other methods:
| Technique | Speed (inches/min) | Time Compared to Laser Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Cutting | Up to 1200 | N/A |
| Bandsaw Cutting | N/A | 10 times slower |
| Wire Cutting | N/A | Up to 100 times slower |
| Plasma Cutting | N/A | Usually slower |
| Water Jet Cutting | N/A | Usually slower |
Bending and Forming
Bending and forming turns flat metal into curves or angles. Special tools can bend the metal without destroying it. The bending radius is important to maintain the strength of the metal.
Advanced tools such as SVM and ANN can help predict the properties of metals. These tools make bending more accurate and reduce errors. For example, SVMs can predict springback. Kickback occurs when a metal tries to return to its original shape after bending.
| Technique | Use | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Support Vector Machines (SVM) | Predicts springback in small bends | Controls springback well |
| Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) | Predicts bending in laser forming | Accurate bending angles |
| Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) | Predicts leftover bends in laser forming | Studies laser effects on metal |
Welding and Joining
Welding and joining join pieces of metal into a structure. The method depends on the material and the strength required for the joint. Common methods are TIG welding, MIG welding and spot welding.
| Welding Method | What It Does | Where It’s Used |
|---|---|---|
| TIG Welding | Uses a tungsten electrode and gas for clean welds. | Cars, buildings |
| MIG Welding | Uses a wire electrode for fast and easy welding. | Large projects |
| Spot Welding | Uses electric current to join points. | Car making |
TIG welding is precise and solid for fine work. MIG welding is faster and suitable for large jobs. Spot welding is fast and suitable for automobiles. Choosing the right method ensures a strong and durable joint.
Stamping and Punching
Stamping and punching are the primary methods of sheet metal fabrication. These techniques form or cut sheet metal into specific shapes. Stamping uses a press and die to form or cut metal. Punching removes excess material by punching holes or making cuts.
Stamping is the best way to make many identical parts quickly. It can save time and money. Punching is great for detailing or functional holes. Both methods require precise tooling to ensure accuracy.
For example, stamping can create parts with tolerances as small as ±0.001 inches. This ensures that parts fit perfectly in larger assemblies. Stamping is also highly accurate, so it is also suitable for industries such as automotive and electronics.
Advanced Techniques (e.g., Waterjet Cutting, CNC Machining)
Methods such as waterjet cutting and CNC machining can improve sheet metal processing. These techniques are highly accurate and efficient.
Waterjet cutting uses a strong stream of water mixed with an abrasive to cut metal. It not only avoids heat but also prevents deformation of sensitive materials. CNC machining uses computer-controlled tools for detailed design. It ensures that complex shapes are machined with great precision.
Industries such as aerospace and automotive use these methods to meet their stringent safety requirements. Waterjet cutting and CNC machining also reduce waste, saving resources and money.
- Why use waterjet cutting?
-
- Prevents thermal damage.
- Handles delicate materials well.
- Why use CNC machining?
-
- Create detailed designs with extreme precision.
- Speeds up the manufacturing process.
Increase the quality and efficiency of your projects with these advanced methods.
Materials used in sheet metal fabrication
Common Metals (e.g. Steel, Aluminum, Copper)
There are three main metals commonly used in sheet metal fabrication: steel, aluminum and copper. Each metal has special qualities for different purposes.
Steel is the most common metal because it is strong and durable. The strength of steel is important in construction and automobile manufacturing.
Aluminum is lightweight and does not rust, making it ideal for airplanes and automobiles. Copper has good electrical conductivity and is therefore often used for electrical components.
Here’s a simple comparison of these metals:
| Metal Type | Market Share (2024) | Growth Reasons |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | Largest segment | Strong, durable, recyclable, high demand in building and car industries |
| Aluminum | Steady growth | Eco-friendly, more recycling, popular in car-making |
When selecting a metal, consider how its characteristics match the needs of the project.
Material selection factors (e.g. strength, corrosion resistance, cost)
Selecting the right material requires consideration of the following. Strength is needed for parts that are subjected to heavy loads or pressure. Corrosion resistance helps extend the life of the material, especially in harsh conditions.
Cost is also important because it can affect your budget. For example, aluminum won’t rust, but it costs more. Mild steel is less expensive, but less strong and durable.
Here’s a look at common materials and their properties:
| Material | Cost per kg | Strength | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High | Moderate | Excellent |
| Stainless Steel | Very High | High | Excellent |
| Mild Steel | Low | Low | Moderate |
| Titanium | Very High | Very High | Moderate |
When making a decision, consider how easy the product is to mold, the cost, and where it will be used. Striking a balance between price and performance will help get the best results.
Applications of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Automotive Industry
Sheet metal fabrication is the key to manufacturing automotive parts. It is used for body panels, exhaust pipes and other components. Steel and aluminum make doors, hoods and fenders strong and flexible. These materials extend the life of the car.
Engine components, such as mounts and covers, are made from sheet metal. They withstand high temperatures and vibrations to ensure reliable engine operation. The chassis and frame are made of sturdy sheet metal that supports the vehicle and absorbs the impact of collisions. Stainless steel is heat- and rust-resistant, making it ideal for use in exhaust systems.
Consumer Goods and Electronics
Sheet metal working is very important in the manufacturing of everyday items. It can be used in things like smartphone cases and refrigerator frames. The products manufactured are not only strong but also lightweight.
The sheet metal market in consumer goods is growing rapidly. in 2023, the market will be worth $5.2 billion. By 2032, it could reach $8.7 billion, an annual growth rate of 5.7%.
| Statistic | Value |
|---|---|
| Market size in 2023 | USD 5.2 billion |
| Projected market size by 2032 | USD 8.7 billion |
| Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) | 5.7% |
| Key driver of market | Consumer electronics |
| Demand for lightweight and high-quality parts | Increasing |
This process helps to accurately detail designs. For example, it allows the manufacture of thin, lightweight and sturdy laptop cases. It also helps to manufacture energy-efficient appliances using lighter materials. Products made using this method are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Conclusion
Sheet metal processing drives continuous innovation in manufacturing and construction with its efficiency, precision and flexibility. Every step, from material selection to workmanship, has a direct impact on product quality and longevity. As the demand of the industry continues to grow, choosing a professional sheet metal fabrication service can make your products more competitive in the market.
With advanced equipment and rich experience, we are able to customize high-quality sheet metal solutions for you. Feel free to join our service and let us help your project achieve higher value!