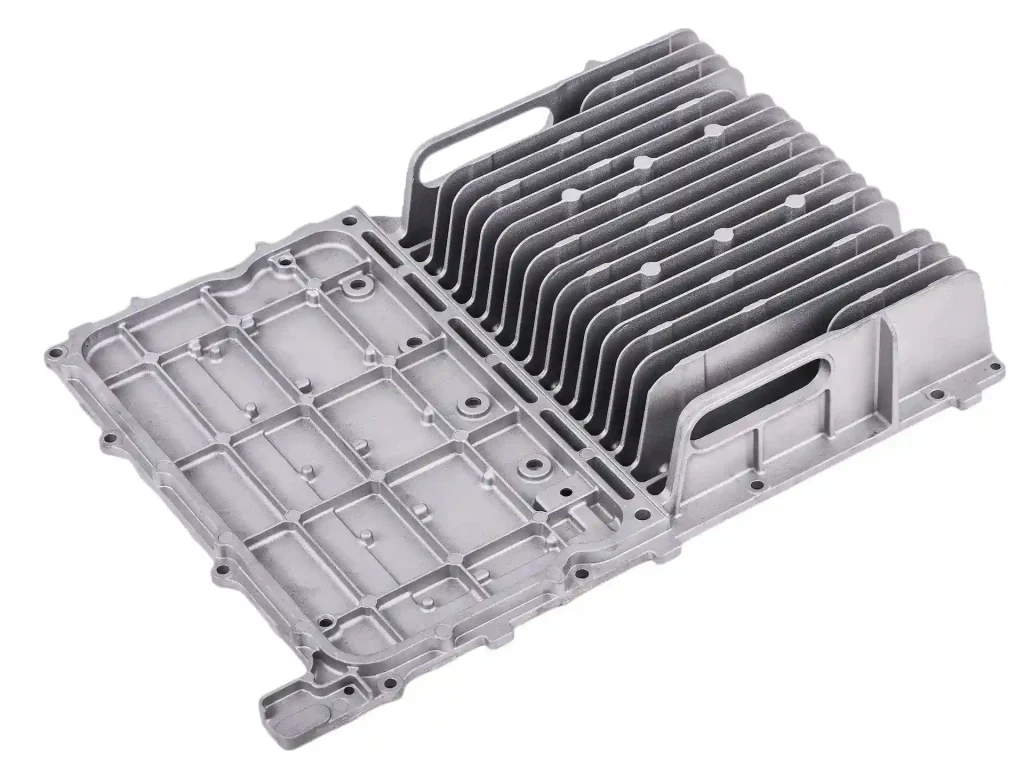
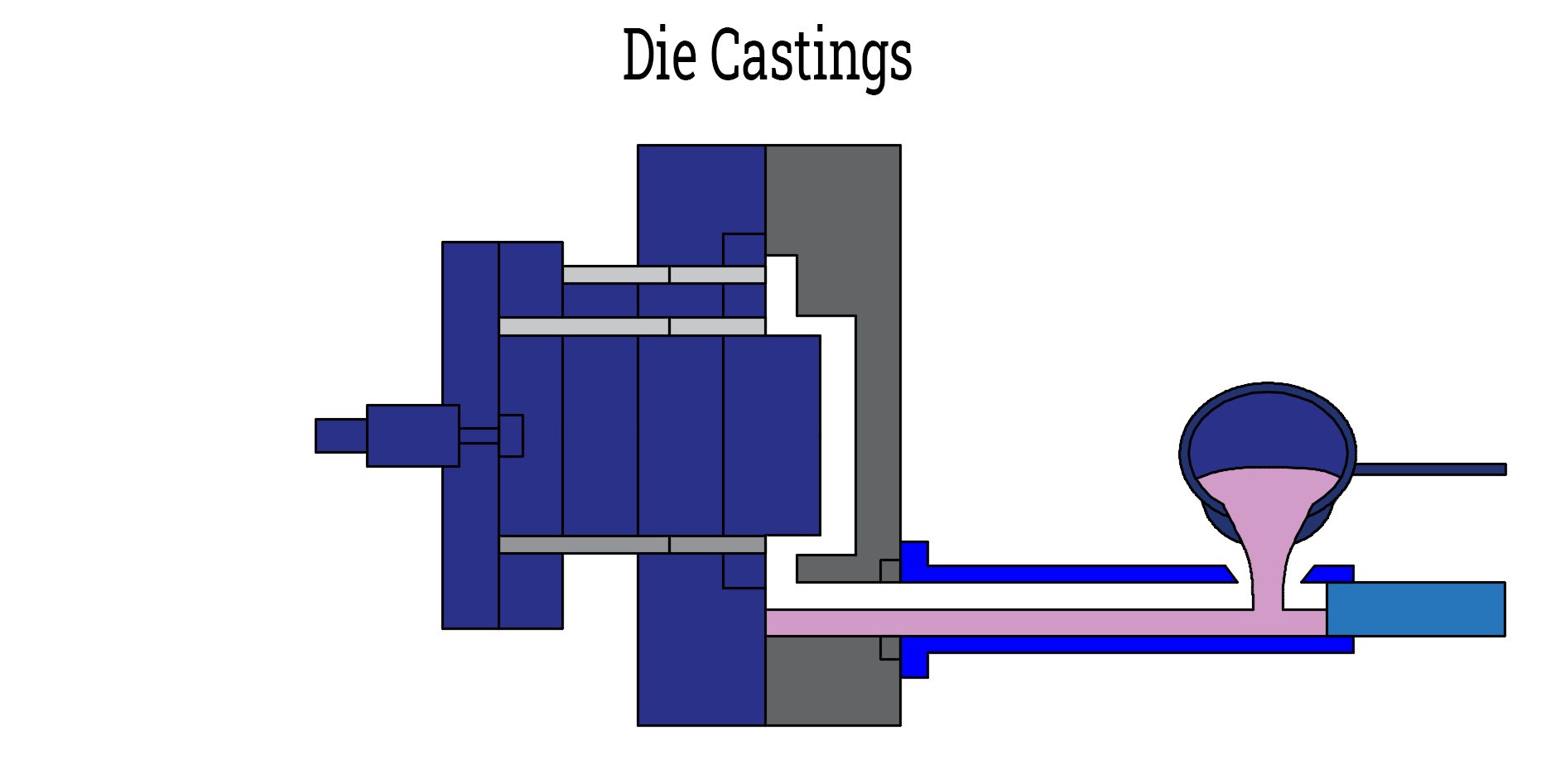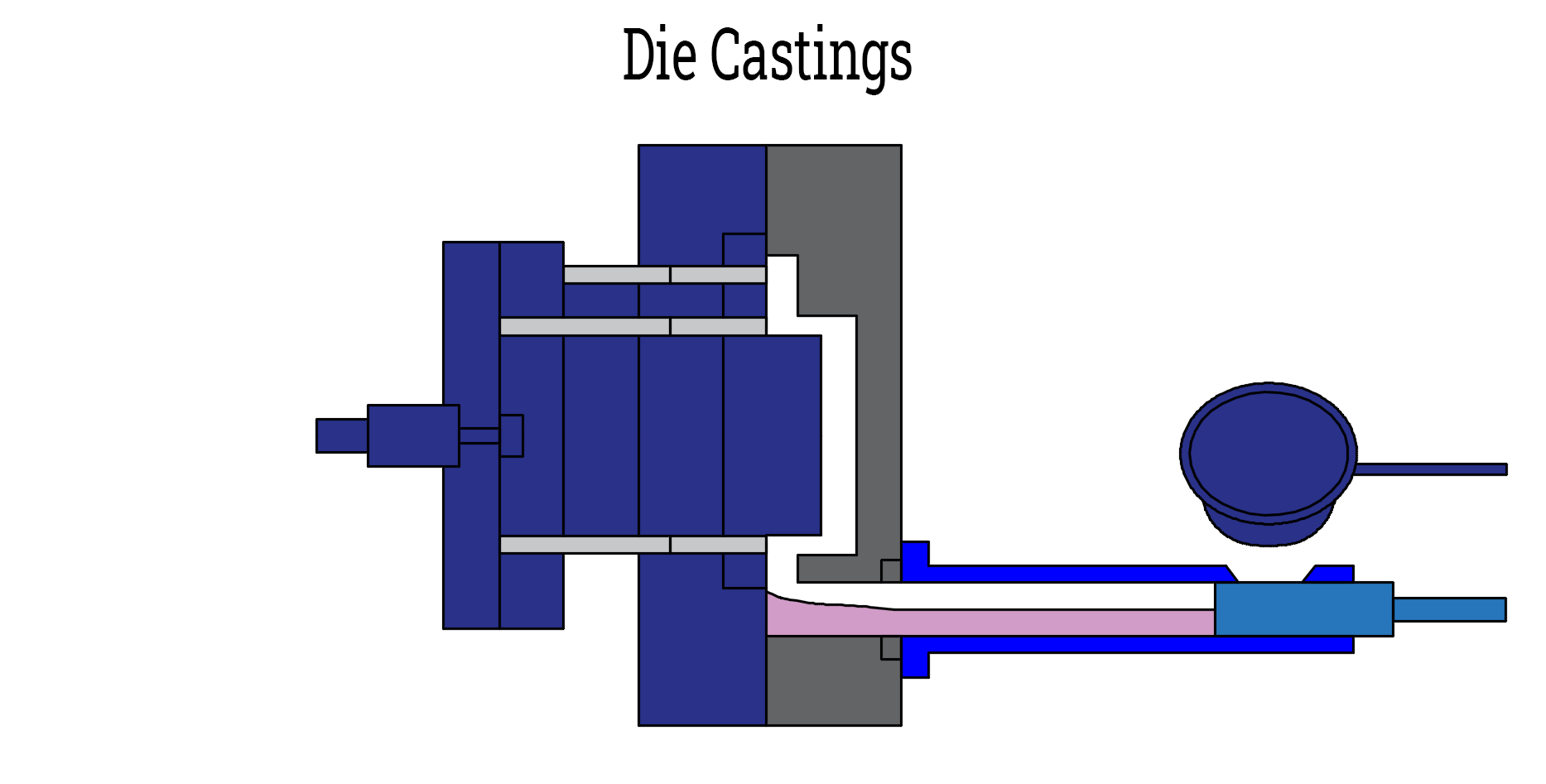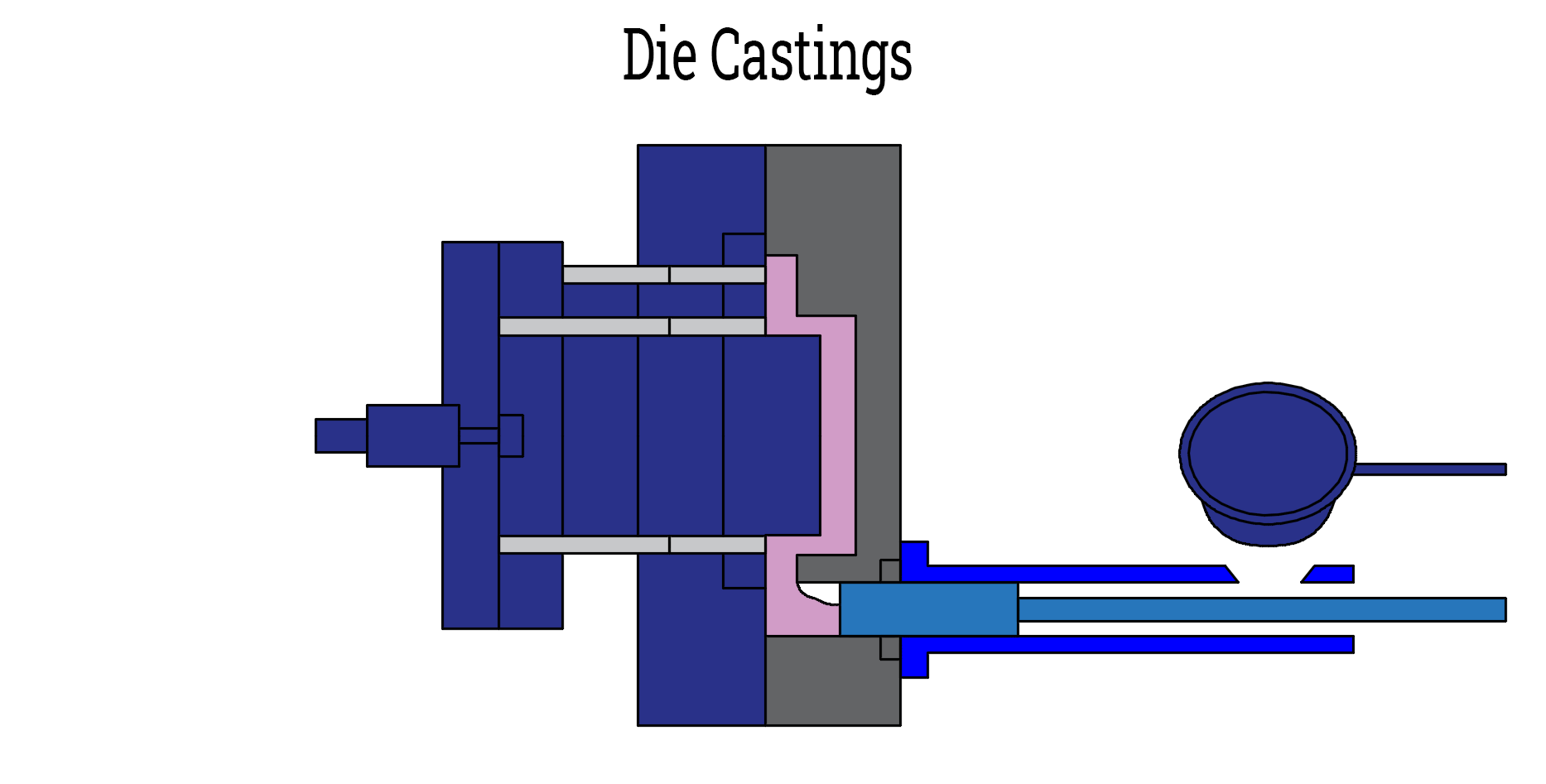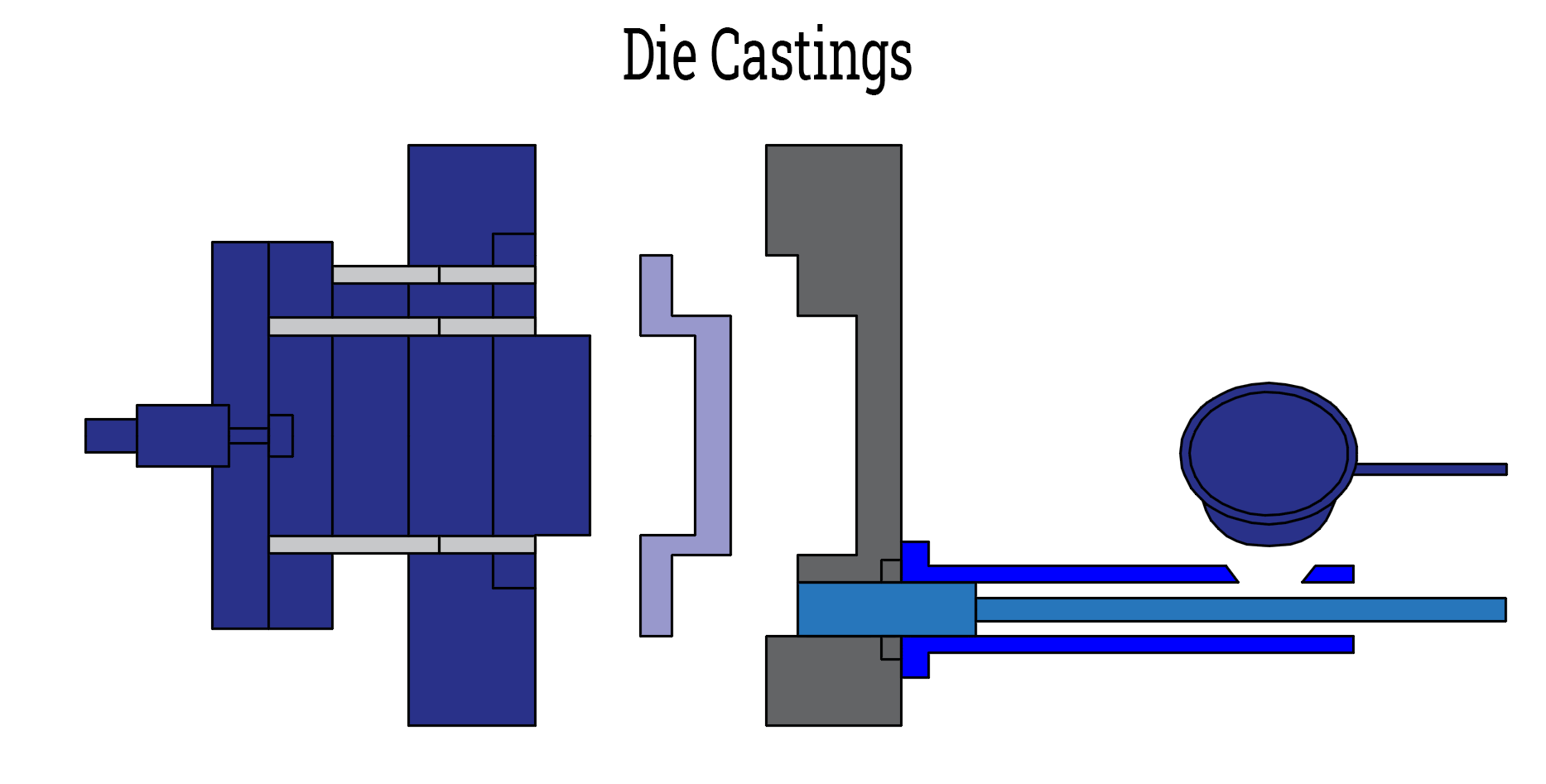
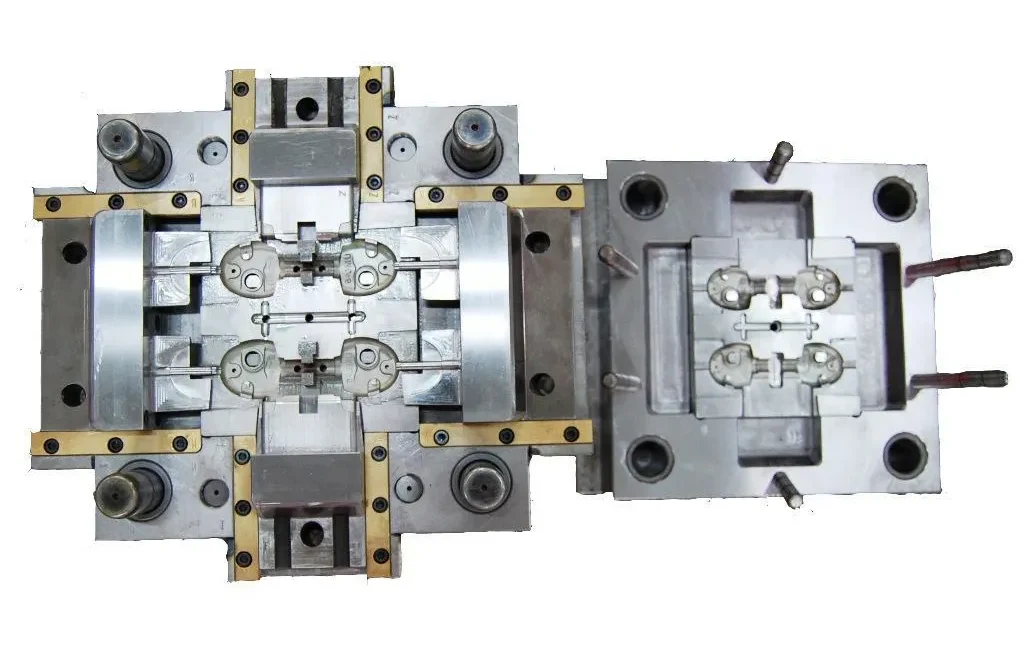
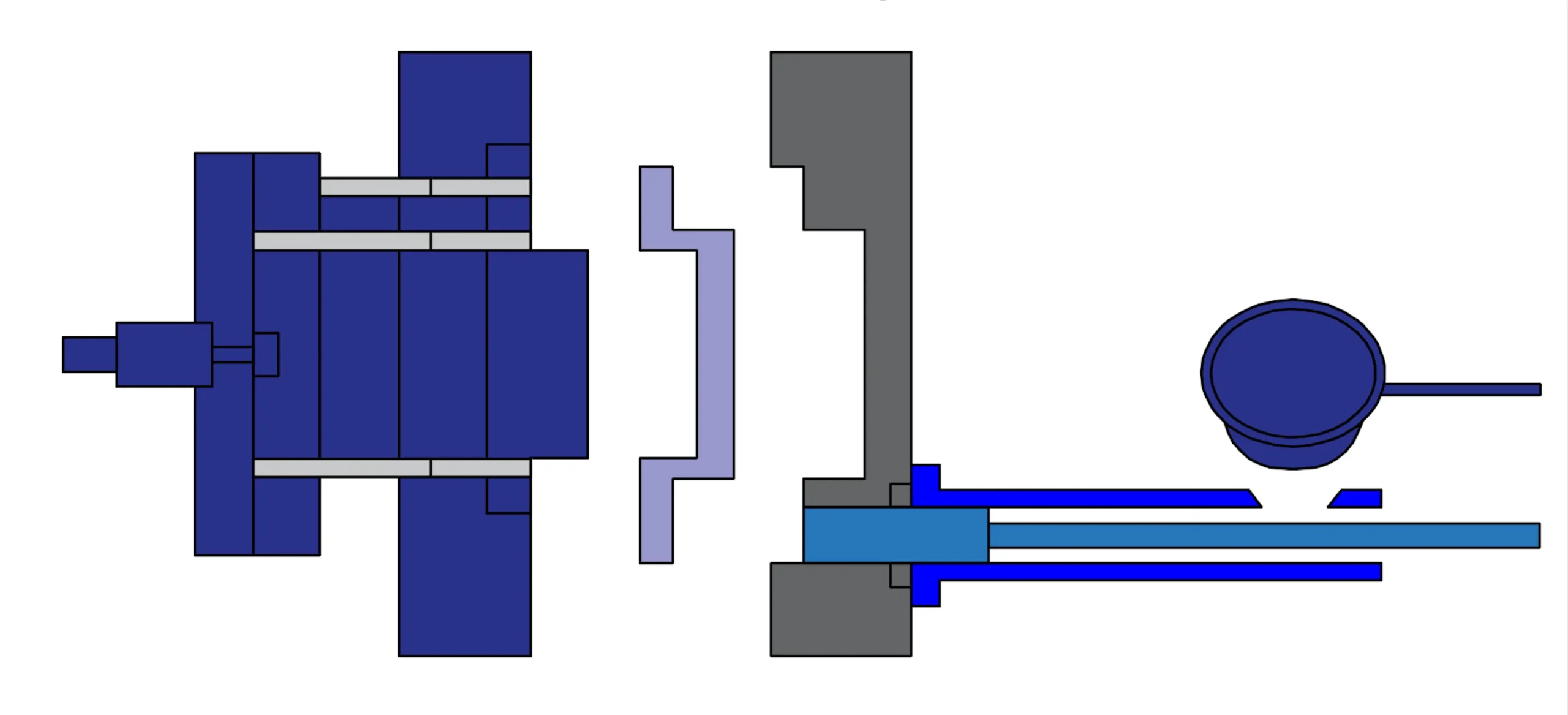
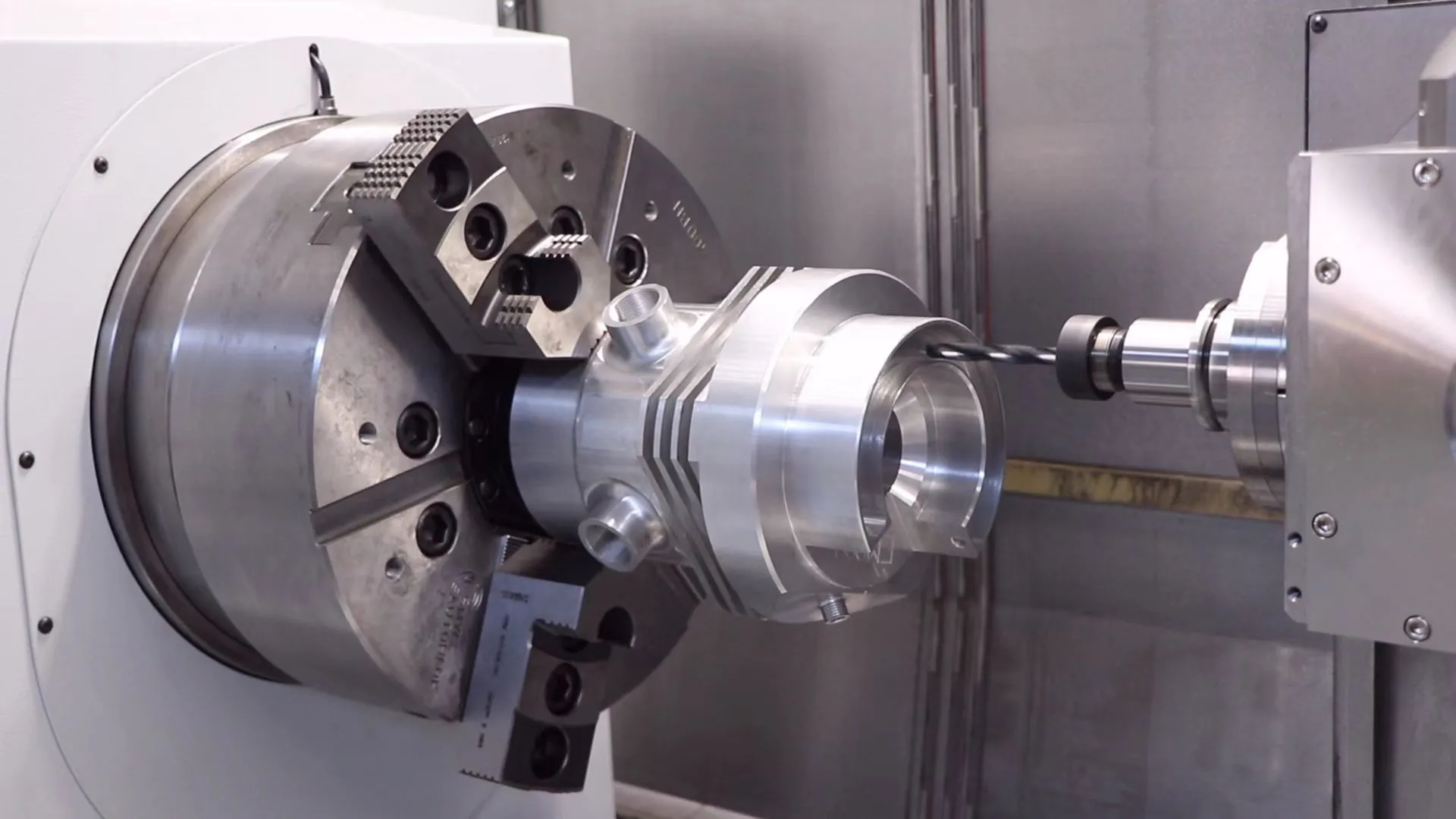
Die casting is a process for making metal parts. It uses strong pressure to push the liquid metal obtained by melting into a mold. This process creates parts that are very precise and detailed. Die casting is therefore ideal for making parts that are hard, complex and in line with the needs of the industry.
It is useful in many areas, such as:
- The automotive industry uses die casting on a regular basis. In 2023, it made up 41.7% of global earnings.
- Airplane makers need it for light and strong parts.
- Everyday products use it to make fancy designs fast and cheap.
The die-casting process is also very efficient. It uses clever designs, high-quality materials and machines to make precision parts. It is popular with modern factories because it not only saves money but also reduces waste.
Key Takeaways
- Die casting is a process that creates precise metal parts by pushing a hot dissolved liquid metal into a mold under high pressure. This creates strong and complex shapes.
- There are two main types of die casting: hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting. Each method is most specific to the metal and the needs.
- Die casting is best for making many parts quickly. It not only reduces waste and lowers costs, but also provides high quality parts.
- Some metals commonly used in die casting are aluminum, magnesium, and zinc. Each metal has different uses in different industries.
- Die casting is important in areas such as automobiles, airplanes and healthcare. It creates parts that meet strict regulations.
How Does Die Casting Work?
Overview of the steps in the die casting process
There are 6 main steps involved in making strong metal parts. Here is how it works:
- Mold design and manufacturing: according to the requirements of the product and the design drawings to create a mold, this part is mainly to CNC machining to complete, the mold first roughing embryo shape, and then polishing the mold to improve accuracy
- Mold Preparation: The manufactured mold is fully cleaned. Add special sprays, such as lubricants, so that the parts are easier to release the mold.
- Injection phase: The molten liquid metal is poured into a sleeve. A piston pushes it into the mold at high pressures ranging from 1,500 to 25,000 PSI.
- Solidification: The mold remains closed while the metal cools and hardens. This maintains perfect shape and prevents mistakes.
- Eject: After cooling, the mold opens and pins push the part out.
- Removal process: Excess pieces of metal are cut off, leaving the part smooth and neat.
Each of these steps is important to creating accurate, sturdy parts. Following these steps will ensure good results every time.
Key Components: Molds, Machines and Molten Metal
Die casting requires three main elements:
- Die Casting Molds: Molds are made of sturdy steel through CNC machining to create precise part shapes. They need to be tested before use and kept in good condition through regular maintenance.
- Die Casting Machine: A machine that pushes hot metal into a mold. Die casting machines are divided into hot and cold chambers, depending on how they work.
- Molten Metal: Metallic materials such as aluminum, zinc and magnesium are melted and poured into a mold to create parts.
These parts work in conjunction with each other to create the perfect product. For example, pins help remove cooled parts and pistons add pressure to fill the mold.
The importance of high pressure in die casting
High pressure is the key to die casting. It is what allows hot metal to fill every part of the mold, even in complex designs. Studies using computer models such as the SPH model have shown that pressure is what improves metal flow. These studies match actual results, proving that pressure is needed for detailed parts.
Without sufficient pressure, the mold may not fill completely. This can lead to problems such as bubbles or missing parts.
Types of Die Casting
There are two main types of die casting: hot chamber and cold chamber. Each type works differently, and different types are suitable for different materials and industries.
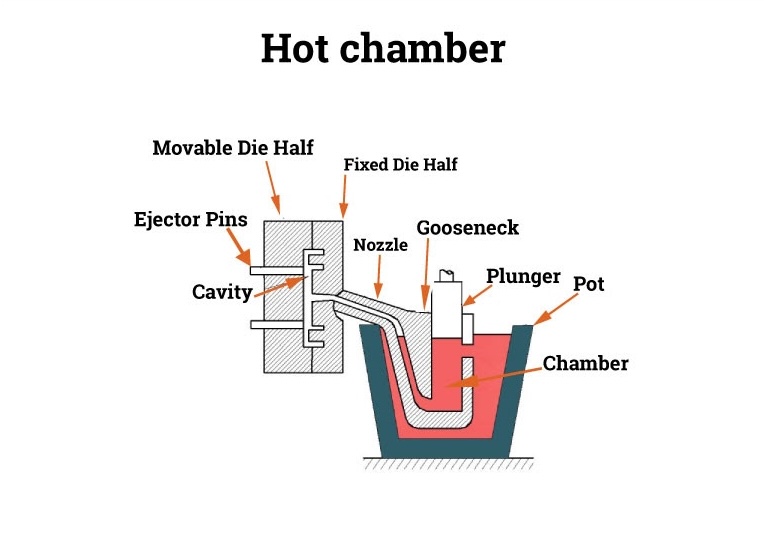
Hot Chamber Die Casting: Principles and Applications
Hot chamber die casting is fast and efficient. Metal is melted inside the machine. A gooseneck tool uses high pressure to push the melted metal into the mold. This method retains heat and speeds up production.
This method is best suited for metals such as zinc and magnesium. These metals melt easily and cool quickly, making them ideal for detailed designs. Industries such as electronics and consumer goods use this method to produce small parts such as connectors and housings.
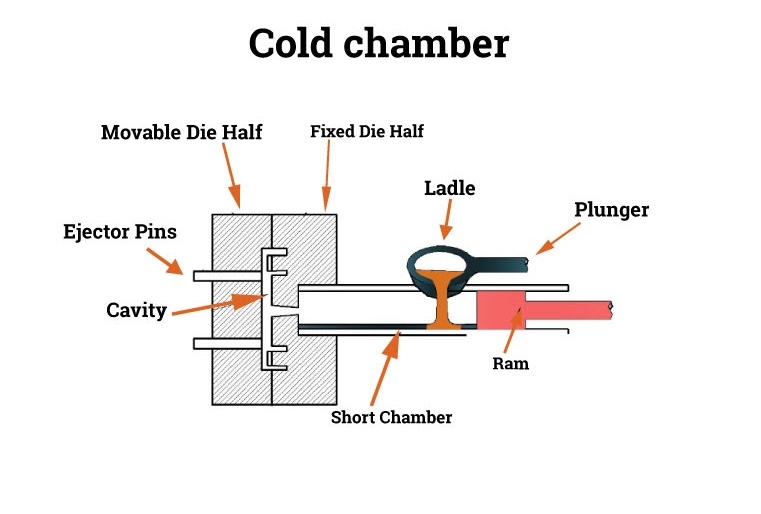
Cold Chamber Die Casting: Principles of Operation and Uses
Cold chamber die casting is slower, but works on a different principle than hot chamber die casting. The metal is melted in a separate furnace. The metal is then scooped into the machine’s chamber. A piston pushes the molten metal into the mold. This method is better suited for metals such as aluminum and brass that require more heat to maintain strength.
It’s slower than slow, but it allows for a wider selection of materials. In the automotive and aircraft industries, this method is used to make strong and lightweight parts such as engine blocks and frames.
Comparing Hot and Cold Chamber Methods
Understanding the difference between the two can help you choose the right method. Here is a simple comparison:
| Feature | Hot Chamber Die Casting | Cold Chamber Die Casting |
|---|---|---|
| Best Metals | Low melting point metals (e.g., Zinc, Magnesium) | High melting point metals (e.g., Aluminum) |
| Metal Injection Method | Uses gooseneck to inject melted metal | Scoops metal into the chamber |
| Pressure Used | 1,000 – 5,000 psi | Similar pressure, works horizontally |
| Mold Setup | Fixed and moving parts | Horizontal setup, no gooseneck |
In hot chamber casting, the chamber is filled with molten metal before casting begins. This will allow for faster casting of low melting point metals. Cold chamber casting starts with a cold chamber and the molten metal is added by hand. This method works better for metals that require a relatively high level of heat.
Both methods are important and useful for different materials and jobs.
Advantages of Die Casting
High Precision and Dimensional Accuracy
Die casting creates very precise and detailed parts. It creates dimensionally accurate parts even for more complex designs. This process reduces the need for additional cutting or fastening. The surface of a die casting parts is smooth and usually does not need to be polished.
High-pressure metal injection fills every corner of the mold. This makes the part not only strong and durable. And die castings can also create thin walls or fine patterns.
Efficiency in Mass Production
Die casting is the best way to produce large quantities of parts quickly. It has a short production cycle, produces large quantities at low cost. The process wastes little material and is also good for the environment. The smooth surface also means fewer extra steps, which also increases efficiency.
Key benefits include:
- Parts are accurate and of consistent quality.
- Short production cycle time, suitable for high volume production.
- Parts are strong with fewer air bubbles.
- Parts are durable, with good strength and resistance.
These features make it the preferred choice for industries that need to produce large quantities of parts quickly.
Versatility of Design and Material use
Die casting is suitable for use with a wide range of designs and materials. It makes it easy to create complex shapes, thin walls and delicate parts. You can use metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium and even titanium.
Die casting offers flexibility compared to other methods:
- It creates thin parts with precise dimensions.
- It works with different metals, both soft and hard.
- Large or complex shapes can be manufactured efficiently.
This flexibility can help industries such as aerospace and automotive to create lightweight and strong parts.
Reduce Waste, Save Money
It reduces costs by using materials wisely.
One of the biggest benefits is recycling surplus metal. In the United States, millions of tons of metal are reused each year. This helps reduce waste and ensures that excess materials are not thrown away.
Using advanced methods also saves money. Automation and lean manufacturing can make work faster and better. These methods help in the following ways
- Reduce wastage of time and materials.
- Ensure product quality and reduce errors.
- Remove unneeded steps to save money and speed up work.
It also saves money by managing waste well. Studies have shown that die casting tends to cost less than other manufacturing methods. That’s why many industries choose die casting technology for great products at great prices.
Choosing die casting means you get strong, accurate parts. It’s also a way to save money and protect the planet. This makes die casting the best choice for today’s factories.
Common Materials Used in Die Casting
Die casting uses specialized materials to create strong and precise parts. Each material has unique features and is used for different purposes. Here are three common materials: aluminum, magnesium and zinc.
Aluminum: Light and Rust-Resistant
Aluminum is the material of choice for die casting. It is very light, making it ideal for automobiles and airplanes. These industries need lighter parts to save fuel. Aluminum is about one-third the weight of steel, which reduces the energy consumption of cars.
This metal is also naturally resistant to rust. It forms a thin protective layer on its surface, keeping it safe from damage. This allows aluminum to be used outdoors without additional coatings. In addition, aluminum is recyclable, which is good for the environment.
You’ll see aluminum in car engines and frames. It is both strong and environmentally friendly.
Magnesium: Strong and Light
Magnesium is known for being strong but lightweight. It is even lighter than aluminum, but can still be durable. This also makes it an ideal material for electronics and airplanes, where weight matters.
Magnesium is easy to machine into thin parts. When mixed with aluminum, it is better at preventing rust. It is commonly used in laptops and car parts where lightweight materials are needed.
Zinc: Tough and Easy to Mold
Zinc is ideally suited for making precision parts. It is characterized by its strong and durable characteristics and its long service life, which saves costs in production. Zinc is also hard and flexible, so it can withstand impacts well. This makes it ideal for parts such as bearings and bushings.
Zinc also has good thermal and electrical conductivity. It is mainly used for small precision parts such as fasteners and connectors. It wastes little material, making it very effective in precision design.
By understanding these materials, you can choose the best material for your needs. This ensures that you get robust and high-quality results for your project.
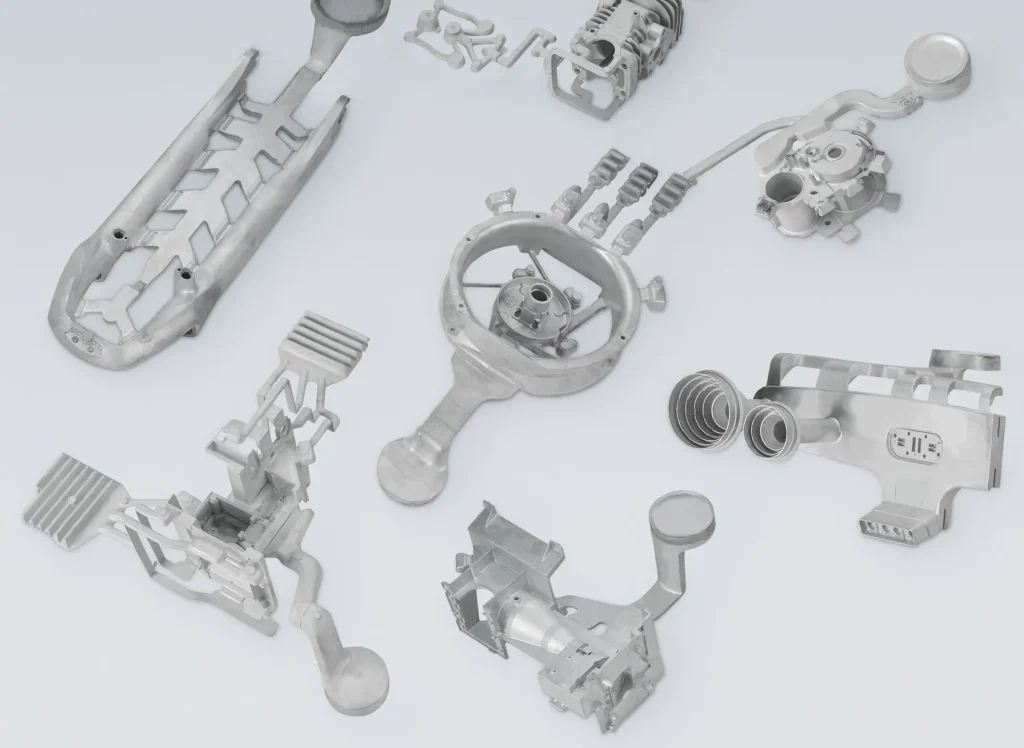
Practical Uses of Die Casting
Die casting is important for making strong and precise parts. It is often used in industries such as automobiles, airplanes, and household goods. This process creates the precise and durable parts needed in these areas.
Automotive industry: engine components and frames
In the automotive sector, die casting helps companies make lightweight and strong parts. It is used to manufacture engine parts such as cylinder heads and blocks. It also makes structural parts such as chassis and frames. These parts must be strong and precise for the car to work properly.
Here’s how the process helps the automotive industry:
| Part Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Engine Components | Needed for lightweight, high-performance parts like cylinder heads. |
| Structural Pieces | Helps reduce car weight and keeps frames strong. |
| Future Growth | Engine parts may grow 8% due to electric car demand. |
Die casting allows for detailed designs with precise measurements. The use of metallic materials such as aluminum and magnesium allows for lighter and stronger parts. This is the key to modern automobiles.
Aircraft industry: Light and robust components
Aircraft require relatively light and robust components. Die castings, especially of aluminum alloys, can help make these parts. These parts are able to withstand stresses while keeping the aircraft lightweight. This improves fuel utilization and performance.
Medical Devices: Precision Device Components
Die castings are important for manufacturing medical device components. These parts must be precise and reliable. Die casting meets stringent regulations and ensures better tools for doctors.
Why Precision is Key for Medical Devices
Medical tools require detailed design and perfect dimensions. For example, surgical tools and scanners require the right parts. Die casting uses high pressure to create precision parts with minimal tolerances. This ensures that each part meets the required standards.
Conclusion
Die casting is very important in today’s manufacturing industry. It creates precise, strong parts while saving time and materials. This process uses metals like aluminum and zinc to create durable items. Industries such as automotive, aircraft, and healthcare rely on it to make quality parts. Among other things, its ability to make delicate parts makes it a top choice for companies.
Future Parts offers exceptional die casting services. Choosing them means getting a fine product that is reliable, affordable, and designed just for you.
FAQs
How Long Does a Die Casting Mold Last?
Molds can be used thousands of times. Steel dies last longer than aluminum dies. Cleaning and maintenance of the mold can extend the life of the mold. This keeps production quality high.
Can Die Casting Produce Complex Designs?
Yes, die casting is great for detailed designs. High pressure pushes metal into every part of the mold. This works well for thin, sharp or complex shapes.
How is Die Casting Different From 3D Printing?
Die casting is faster, cheaper, and can make many parts. It makes stronger, tougher parts. 3D printing is better for testing ideas or making a small number of parts because it is flexible and less expensive to set up.